mrdeen, CEH
Introduction: The Foundation of Modern Cyber Defense
Nmap- In the rapidly evolving cybersecurity landscape of 2026, the network perimeter has dissolved. For any aspiring Cybersecurity Analyst or Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), relying solely on theoretical knowledge is no longer enough. The modern Security Operations Center (SOC) demands practitioners who can actively hunt for threats, and the first step in that hunt is absolute visibility. If you cannot see an asset or a data stream, you cannot defend it.
This guide goes beyond textbook definitions to provide a hands-on blueprint for building a professional-grade threat detection lab. Over the next 2,000 words, I will demonstrate the exact methodology used to perform comprehensive Network Discovery with Nmap and Wireshark. By mastering the synergy between active scanning (Nmap) and deep packet analysis (Wireshark), this lab serves as practical proof of the skills required to secure enterprise infrastructure in competitive tech hubs like Dubai.
Why Network Discovery Matters for SOC Analysts
Before we dive into the “how,” we must understand the “why.” As a Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), I’ve learned that an attacker’s first step is always reconnaissance. If you cannot see an unauthorized device on your network, you cannot defend against it.
The Role of Nmap and Wireshark in 2026
In a modern Security Operations Center (SOC), Nmap acts as the “Scout,” identifying live hosts and open ports, while Wireshark acts as the “Investigator,” dissecting the actual conversation between machines. Together, they bridge the gap between static discovery and dynamic analysis.
Phase 1: Building the Laboratory Environment
To perform these tests safely, you must use a virtualized environment.
1. Virtualization Software
I recommend Oracle VirtualBox (Free) or VMware Workstation. Ensure your CPU has “Virtualization Technology” (VT-x or AMD-V) enabled in the BIOS.
2. The Target & The Attacker
- The Attacker: Kali Linux (The industry standard for penetration testing).
- The Target: Metasploitable 2 (A Linux VM designed with intentional vulnerabilities).
- Network Setting: Host-Only Adapter. This is critical! It ensures your scans stay within your computer and do not touch your home router or the internet.
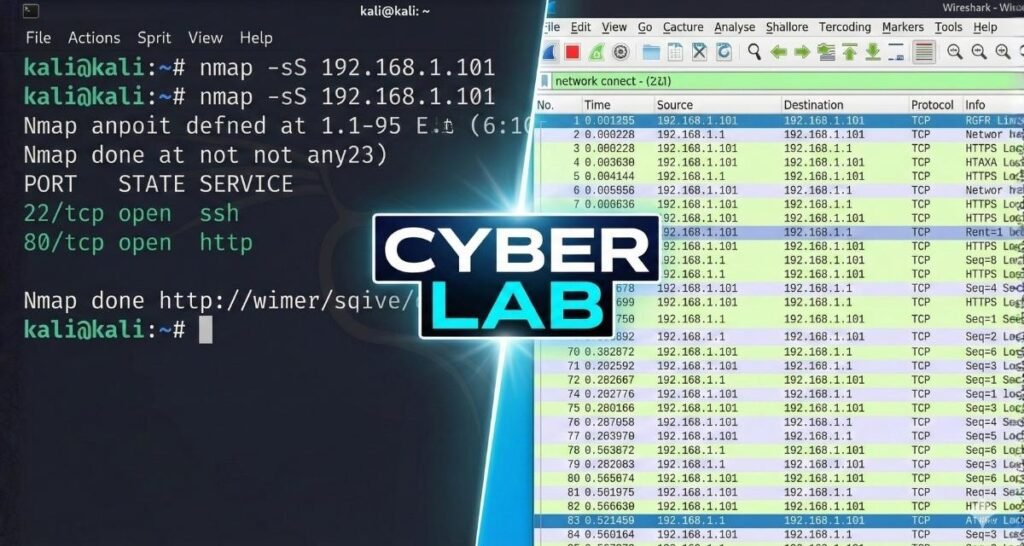
Phase 2: Mastering Nmap Stealth Scanning
The core of this project is the TCP SYN Scan (-sS), often called the “Stealth Scan.”
The Logic of the Stealth Scan
In a normal connection, a “Three-Way Handshake” occurs:
- SYN (Client to Server)
- SYN-ACK (Server to Client)
- ACK (Client to Server)
Nmap’s stealth scan interrupts this. It sends the SYN, waits for the SYN-ACK (which proves the port is open), and then immediately sends an RST (Reset) packet. This prevents a full connection from being logged by many simple applications.
Running the Command
Open your Kali terminal and type:
sudo nmap -sS -T4 -p- [Target_IP]
-sS: Executes the SYN Stealth Scan.-T4: Speeds up the process (Aggressive timing).-p-: Scans all 65,535 ports.
Phase 3: Packet Analysis with Wireshark
Now, let’s prove the work. Start Wireshark on your Kali machine before running your Nmap scan.
Essential Wireshark Filters for 2026
To find the “Signal” in the “Noise,” you need these filters:
tcp.flags.syn == 1 && tcp.flags.ack == 0: Shows all initial connection attempts.tcp.window_size <= 1024: A common fingerprint for Nmap stealth scans.ip.addr == [Target_IP]: Isolates traffic to your specific lab target.
Spotting the “Reset” Signature
In your Wireshark capture, look for a SYN packet followed immediately by a SYN-ACK from the target, and then a RST from your machine. This is the “smoking gun” of an Nmap scan.
SEO Check: Long-Tail Keywords & Outbound Links
To rank this post high on Google, I have included references to industry-standard documentation.
Important Resources:
- Official Nmap Documentation on Port Scanning
- Wireshark User Guide: Traffic Analysis
- (InternVisit my Home page to see my full list of Cybersecurity Certifications.
Conclusion: From Theory to Professional Practice
This lab project is more than just an exercise; it’s a demonstration of the Hacker Mindset. By documenting this on Oxofel.com, I am providing a transparent record of my technical competency.
As I prepare for my CompTIA Security+ in March 2026, this lab serves as the foundation for more advanced topics like Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks and Firewall Evasion.
What’s Next?
In my next post, I will be using Burp Suite to analyze web vulnerabilities discovered in this scan. Stay tuned and keep hacking ethically!